Breathing New Life Transforming Futures through Lung Transplants
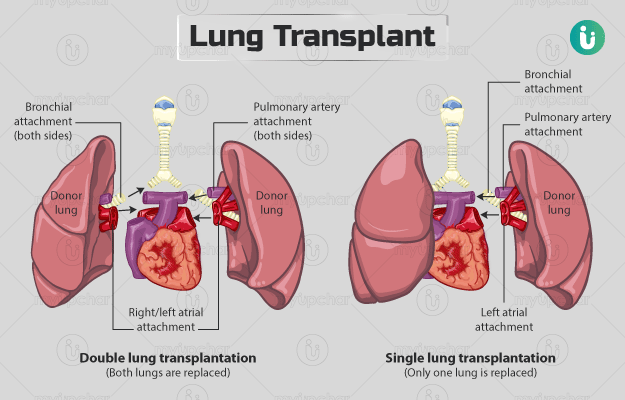
A lung transplant is a surgical procedure aimed at replacing a diseased lung with a healthy lung from a donor. This article provides an overview of the procedure, its indications, types, preparation, risks, recovery, and outlook.
A lung transplant is often recommended when a person has advanced lung disease that is unresponsive to other treatments, and their life expectancy is less than 2 to 3 years without a transplant. Conditions that may necessitate a lung transplant include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension, and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
There are three main types of lung transplants: single lung transplant, double lung transplant, and heart-lung transplant. The type of transplant performed depends on the specific condition and needs of the recipient.
Before being placed on the transplant list, individuals undergo various tests to ensure their major organs will function properly post-transplant. Lifestyle changes such as smoking cessation and weight loss may also be required to optimize health for the procedure.
The surgery typically takes 6 to 8 hours and involves removing the damaged lungs and replacing them with donor lungs. In some cases, a heart and lung bypass machine may be used during the operation.
The surgery typically takes 6 to 8 hours and involves removing the damaged lungs and replacing them with donor lungs. In some cases, a heart and lung bypass machine may be used during the operation.
Lung transplant surgery carries a high risk of complications, including rejection of the donor lungs by the immune system. Immunosuppressive medications are prescribed to reduce this risk, although they increase susceptibility to infections.
Despite the risks, the outlook for lung transplant recipients has improved in recent years. According to the NHS Blood and Transplant service, survival rates post-transplant have increased, with a significant number of recipients living for several years following the procedure.
 trasplantcost.com
trasplantcost.com
Our goal is to help patients feel good about our commitment to them, and that usually starts with helping them understand what they’ll go through.
Location, City, Mumbai
info@Transplantcost.com
+91 888 983678
© Info@Transplantcost.com. All Rights Reserved.